Author of the article:
Fastening elements are widely used in construction, mechanical engineering, other industries and in everyday life. These products are presented in a wide range and allow you to solve various technological problems. Therefore, it is necessary to have an idea of what types of fasteners exist.
The main types of fasteners used today include:
- screws and self-tapping screws;
- anchor fasteners;
- metric fasteners;
- rivets.
Let's take a closer look at the main types of fasteners, their purpose and scope of application.
General information about fasteners
Classification of standards systems
- GOST, developed and adopted in production since the end of 1980 on the territory of the USSR. Subsequently, they did not revise it. In addition to the existing values, modern developments adopted in the territories of the CIS countries are added. The capital letter of the name of the corresponding state is added to the GOST abbreviation.
- The DIN standard system has existed in Germany since 1952 and is recommended throughout Europe.
- ISO, these standards combine all the new developments of fastening hardware manufacturers in European countries, England and the USA. All values are fully adapted to the DIN system worldwide
- EN is a code of purely European fastener standards, but completely oriented towards the ISO system.
To avoid confusion, the digital indices are left as is.
Why are fastening hardware needed?
With their help, several types of parts connections are obtained:
- Detachable connections are made using bolts, nuts, washers, threaded rods, screws, self-tapping screws. These are multi-use connections.
- Hard connection. Achieved using rivets.
Application area
- Mechanical engineering.
- Car production.
- Production of electrical products.
- Construction.
- Furniture manufacturing.
Division by material of manufacture
- Steel fasteners. Various grades of steel are used in their production depending on the application of the product.
- Stainless steel fasteners, parts are used in chemically aggressive environments and with high humidity.
- Aluminum hardware. These are mainly rivets and rarely a certain type of nail.
Metal cable
A steel cable consists of several wires twisted into a strand. This plexus twists onto the central rod. The number and size of wire determines the level of corrosion protection and abrasion resistance. Smaller diameter cables have better flexibility and movement. The braid consists of several individual wires that are wound around a base in one or more layers.
There are several types of cables, differing in the type of wire weaving:
- universal: wires of the same section are connected;
- parallel: wires of different sizes are connected, maintaining the same number of wires in the outer and inner layers;
- filler: twice as many external wires as internal. Smaller wires fill the gaps between larger wires;
- compacted: created by increasing the fill factor.
There are also hardware that can minimize the tendency to rotate. To achieve these goals, experts recommend using low-rotation metal cables or models that demonstrate resistance to rotation. Such cables consist of several layers of wire. Layers are applied in the opposite direction to the next layer. Due to this, it is possible to maintain opposing forces in the cable.
Electrodes
Electrodes are excellent conductors of electricity. When studying the concept of "electrode", you need to consider the cathode and anode. The cathode is the current leaving the electrodes. The anode gives off electrodes, and it is on it that the oxidation reaction occurs. The electrode does not have to be metal. There are inert and reactive electrodes. The main difference is that reactive electrodes actively participate in processes, while inert electrodes are a passive type. Reactive electrodes can include zinc, copper, lead and silver, inert electrodes can include platinum, gold, rhodium. Electrodes are considered important elements in electrical connections because they enable the transfer of electrons from one source to another, creating an electrical charge.
The main use of electrodes is to create an electric current and pass it through non-metallic objects. Electrodes are also used to measure conductivity.
Washers
Washers increase the reliability of threaded connections. They also protect the surface when installing fasteners. This type of hardware distributes pressure and prevents movement and corrosion at the joint.
There are 6 main types of washers, although there are a large number of subgroups. The basic categories include:
- flat washers. Ways to distribute the load on a joint, reducing heat and friction during the fastener tightening process. In the industrial sector, this type of hardware is used as a substrate for a safe and reliable connection. Another use for flat washers is for electrical insulation;
- Lock washers are found in the automotive industry and are used in the production of household appliances. Such hardware is suitable for connections in moving mechanisms. For example, if the fastener is subject to vibration;
- shoulder washers. Used as a spacer to insulate fasteners. Such hardware is most often made from non-conductive materials. Shoulder washers are not used in wet environments;
- countersunk head washers. Most often found in the furniture industry. Aesthetic washers that have a countersunk head;
- spring washers. They apply an axial load to the fasteners in the event of vibration or thermal expansion, thereby avoiding fastener movement. They are made of metal. They are often replaced with springs due to their light weight and miniature size.
Facade fasteners
In recent years, more and more attention has been paid to the thermal and waterproofing of building facades, the safety and reliability of which largely depends on the fasteners used. Their choice should first of all be made based on the type of load-bearing foundations.
The first group is porous solid bases. These include aerated concrete and gas silicate blocks. Such foundations are highly susceptible to destruction under constant pressure. Therefore, it is not practical to use fasteners based on friction force for such buildings. The special shape of the sleeve allows you to avoid significant pressure on the material. Thanks to it, so-called “pockets” are formed in aerated concrete, working on the shear of the material, and not on expansion.
The second and third groups are strong solid and hollow foundations. Solid bricks include concrete, solid silicate and ceramic bricks; hollow bricks include alkali bricks and expanded clay concrete blocks. For such bases, dowels that use friction force are more suitable.
Self-tapping screws with drill
– the most convenient elements of façade fastening.
They do not require pre-drilling a hole, which significantly saves time. If you have to deal with thin sheet steel, sharp self-tapping screws with a press washer
.
Screws for sandwich panels do not require pre-drilling. Their purpose is direct installation on steel structures. To ensure the greatest reliability, hardware is made from hardened carbon steel, and to avoid corrosion it is pre-galvanized.
The shape of the part head is no less important. It directly affects how the dowel perceives and subsequently transfers the load to the load-bearing base. Particular attention should be paid to this point when installing thermal insulation boards.
Thus, dowels for thermal insulation (disc-shaped) expand in 3 directions and provide the tightest installation. They can be either with a plastic or metal nail. Moreover, the metal nail must be galvanized in order to avoid corrosion and increase the durability and reliability of the building’s thermal insulation.
Groups of fastening hardware
Fastening hardware is also divided into two subgroups.
The first is products where the carving is made to a strictly defined size. They are also called metric fasteners. This includes washers, bolts, nuts and studs. Each of these elements may have its own thread pitch, but usually craftsmen adhere to GOST.
The second group includes hardware of various shapes. Here you can see screws, screws, screws and nails. But that’s not all.
It is important to consider that each fastener is developed for specific purposes, and therefore it is strictly forbidden to confuse them or use them according to other standards.
Today, metallurgy every day develops more and more hardware used in everyday life or in production. We are constantly working to improve materials and final products. The overall quality gradually increases and the speed of work increases.
The competition between two similar events is developing seriously. Each company is interested in finding absolutely unique methods for manufacturing hardware and winning the trust of customers. For example, the PKM company supplies high-quality fasteners from the world's leading manufacturers. Sales are carried out in St. Petersburg and throughout Russia. More details at https://pkmetiz.ru/.
Staples
This type of hardware is used according to the principle of a nail. The brackets are U-shaped elements. They are mounted in soft surfaces of structures. The staples are designed for wood joints, MDF or plywood. For convenience and proper installation, use a construction stapler. It can be used to make reliable connections. Staples are often used in construction and furniture assembly.
Type of fastenings used during construction
Plasterboard assemblies usually have the following composition:
- Gkl (plasterboard sheet)
- Metallic profile
- Wooden spacers
The variety of materials used subsequently leads to the need to consume different hardware.
What tools are used to work with hardware?
There are only 6 main tools that are actively used when working with hardware:
- A hammer is necessary when using nails and screws.
- A screwdriver is needed to use self-tapping screws and screws for their intended purpose. You can also use it to work with small screws and bolts.
- Screwdrivers are indispensable when you need to screw in screws or screws.
- Wrenches will be needed when you have to work with bolts and studs with nuts installed on them.
- Drills and hammer drills will be needed in cases where you need to drill several holes for anchors.
- Finally, pliers are most often used when you need to hold and bend anchor plates.
Various machines can be classified into these same groups, but they are rarely used and are needed mainly for production purposes.
Metric fasteners
Metric fasteners are usually called fasteners whose parts have metric threads. These include nuts, washers, screws and bolts. The scope of application of the parts is very wide: from household and construction work to aircraft and automotive industries.
screw
- a square or hexagonal part with a threaded hole. Its purpose is to provide reliable and durable fastening.
Washer
It is a ring part placed under the head of a bolt or nut.
Screw
It is a threaded rod ending in a cap on one side. Varieties without a cap are usually called hairpins. Screws are divided into “responsible”, they are used to fasten parts made of hard materials, and “non-responsible”, for example, self-tapping screws, intended for fastening parts made of soft materials.
Bolts
- a fastener in the form of an external threaded rod, usually ending in a hexagonal head. They are used exclusively in conjunction with a nut and are divided into varieties with full and incomplete threads.
The main advantages of Ficher metric fasteners are: increased strength of fasteners, ease of installation and dismantling. And the main feature that distinguishes metric threads from numerous other varieties is the triangular profile, the angle of which is 600.
The thread parameters of metric fasteners are measured in millimeters and are designated by the letter “M” in combination with a number. So, M8 means metric thread, the diameter of the rod of which is 8 mm.
The thread pitch is also important - an indicator that determines the distance between adjacent turns. Measured using a thread gauge. A large step is considered the main one and is not indicated; small ones are usually marked as follows - with an “x” sign in combination with a number. For example, M8x1 means metric thread with a pitch of 1 mm.
Metric fasteners https://fikser.ru/catalog/metrika/ from the manufacturer Fiхer are sold in Moscow; they can be purchased in bulk at an affordable price. It is possible to order delivery.
Metric Fastener Torque Procedure
Any fastening connection must first of all be reliable and durable. This is achieved by many factors, but one of them is control of the installation force (tension) when tightening the fastener elements. Experience shows that overstressing a connection, or not tightening it enough, can cause it to break.
To avoid such situations, several methods have been adopted in the industry to control the quality of connections. They are based on measurements:
- Extension of a screw, bolt or threaded rod.
- Torque when tightening the nut.
- The angle of twist of the nut.
The most accurate results are achieved when using the elongation measurement method. It is most often used in particularly critical connections, with high stress on the thread.
If these are threaded rods, then the elongation coefficient of the rod can be measured during loading. To do this, measure the distance from the end of the pin to the plane of the base to which it is attached.
To control the tightening force of a threaded connection, various intermediate elastic inserts (like a spring washer) can be used. Such a washer is placed under the nut and tightening is stopped at a certain moment. Or they install a so-called measuring washer, which differs in thickness from a regular washer and is deformed when twisted.
Abroad, they sometimes use a shaped washer that has a bent chamfer. It is placed between the surface and the bolt or screw, and as it is tightened, the field of the washer seems to shrink under the weight of the bolt. At first it is in close contact with the bolt and as it is tightened it can reach the surface of the part. This way you can easily control the tightening torque.
In the case of particularly critical connections, their tightening can be checked using ultrasound.
The last method is to measure the angular twist of the nut. In this case, it simply indicates how many degrees the nut should be turned for the most accurate connection. Installation of nuts with this requirement is quite easy using templates or special angle gauges with an accuracy of 10 ... 15°.
The method of measuring by the angle of rotation of the nut is the best, because it has nothing to do with the resistance force of the materials, their friction against each other, etc. In addition, this is the simplest method, since it does not require any special (and often complex) devices or tools.
However, even this is not always effective, because there may be difficulties in determining the initial angle, or you will not be able to correctly assess the resistance of materials to friction, as well as take into account the initial gap between the body of the part and the head of the bolt or screw. The accuracy of the tightening force when controlled in this way is no more than ±20%.
This method is also not suitable for connections with short bolts, because the angle will be very small and may simply not be achieved. And the error will be much higher.
The most practical method in production is still considered to be the method based on the use of torque wrenches. They are set in advance to a certain load level and the fastening will be the same for all structural elements. The torque wrench measures the applied torque, and when the limit value is reached, tightening stops automatically.
There are also so-called limit keys, in which release clutches, or friction clutches, operate (i.e. load limiters). At the moment the maximum load value is reached, such a key stops working or gives a special signal. This also requires preliminary calibration of maximum effort.
What is the strength class of metric fasteners?
By default, the strength class of metric fasteners is 5.8. all other strength classes (8.8; 10.9, etc.) must be discussed with the manager. Also, by default, all bolts have full threads and are also galvanized, and incomplete threads or fasteners without coating are negotiated separately.
Types, classification, varieties of hardware
Now we move directly to species diversity. As we said, all factors are based on the application and purpose. Conventionally, it is customary to distinguish two large groups. The first is metric. Its main feature is its strictly regulated form. These are samples that are ideally suited to one competitive type of production. And they are subject to standards of composition, impact strength, and environmental resistance. They also have strict dimensions, length, width, height, thread pitch, thickness of the main components. This group is represented by bolts, nuts, and studs in wide variations.
But the second is situational non-standard options. Anchors, screws, rivets of all types. With this group, everything is somewhat more complicated, because there are no established regulatory standards for them. Therefore, here the importance of the supplier becomes even more serious. After all, it will not be possible to check the quality simply using the accompanying documentation, which contains GOST stamps.
Let's move on to analyzing each individual product.
Bolts
Initially, these included any metal products with an oblong configuration and without cavities. But now there is strict regulatory documentation, where this concept means an elongated product with a thread. It is fastened in two ways - either by screwing it into a groove, or by means of a nut - an intermediate element.
According to the shape of the head, it is customary to distinguish between classic, hexagonal, and semicircular. This also includes anchor, folding, flange. As we have already said, what hardware means is fasteners in their purest form. And the bolt is the first thing that comes to mind when talking about fixation. And statistics agree with this statement, because it is the absolute leader in both application and production. Specifically, in the construction of railway tracks, a lot of different bolts are used, which differ in shape and size, as well as in purpose. We will talk about each of them in more detail below.
Hairpins
This part has one significant difference from the previous one - the absence of a head as such. That is, the thread is applied along the entire length of the rod without visible transitions. And such a part is secured in most cases with a nut, and not simply by screwing it into the slot. After all, there is no limiter in the form of thickening.
This variation is used in almost every field, but in a narrow area. Therefore, the volume of purchases of parts of this kind is usually small. To better understand exactly how a pin works, look at the photo of hardware and fasteners.
screw
Actually, here is the element that fixes the previous two. At its core, it is auxiliary. It is screwed onto a thread onto the base, for example, in the form of the same hairpin. The important point is that the nut must exactly match not only the dimensions, but also the thread pitch of its base. And also be of the same hardness category as the rod. Otherwise, under heavy loads, which are often created by passing trains, it is the nut that will fail. If it is inferior to the rod in terms of strength, it will simply break or bend it. Also, if the tightening is not completed completely, then due to vibration the part begins to gradually unwind. This will all end with the fasteners simply coming out of the groove at the most unfavorable moment. What could cause an accident.
Washers
Just to prevent the possibility of unscrewing the part on your own, we need this sample. When analyzing what constitutes hardware, it is difficult to list all the variations. But these big three are always named among the first. Bolt, nut and washer. The latter is a ring part that is installed under the screwing surface. Usually between the stop and the nut. This increases the contact area and distributes pressure more evenly, eliminating deflections and deformation. And the reverse movement of the clamps will be blocked.
It’s worth warning right away that the presence of a washer is not a panacea, because strong vibration can still unscrew the lock. But this reduces such cases by almost half. This means that in any collection of fasteners for railway tracks it must be included.
Travel crutch
If you study what names there are for hardware, this is the most ambiguous. After all, this part was previously called a nail. And now it is periodically called that way. In fact, this is true, because the product is a large nail with a branched side head. The main purpose is to fasten rails and railway sleepers. In new path variations this element is rarely used. But it’s worth knowing that at the moment in the Russian Federation, almost 85% of all roads are old versions of railways. And there are crutches installed there, and they are also used during repairs.
Track screws
Let's move on. Let's look at the following hardware products, what they are - track screws. This is a large fastener with a square head for screwing with a key. But now special screwdrivers for track screws are increasingly being used. Recently, many variations of these products have appeared. Various rods, head shapes - not only four, but also six or more faces.
The standard length of 175 mm is often used. But longer variations are also common, up to 190 mm.
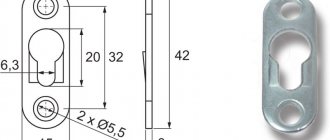
PC terminal
The part is used exclusively for fastening the rails to the lining in joints of the KB and KD types. This is one of the parts of the assembly where the main latch is, respectively, a terminal bolt of a suitable size and diameter. The terminal itself is installed on it. The part is subject to stringent requirements for withstand temperature, pressure, mechanical shock, and most importantly, vibration.
Screws and self-tapping screws
These two types of fasteners can be classified into the same category, since they have a similar design and scope of application. In essence, a self-tapping screw is the same screw, but in a modern design and with a number of advantages. So, to fix it with a screw, you must first drill a hole, and only then screw in the fasteners. The self-tapping screw, in some cases, copes with the drilling task itself and is screwed in without additional preparation of the seat. A screw, even one made of hardened steel, does not have a sharpening point on the threads, so even when using it to connect two wooden elements, you must first prepare them.
Structurally, these hardware look similar, with the exception of the threads. With a screw, it is most often incomplete, that is, part of the body remains smooth, although there are screws with a full thread. The self-tapping screw, if it is small, is completely covered with threads. The main purpose of screws is to fasten wooden elements, while the self-tapping screw is capable of working with metal elements, which significantly expands the scope of its application. Self-tapping screws for metal and wood differ in size and thread pitch: hardware for wood has a wide thread with a large pitch, and metal hardware has a small spiral with the shortest pitch.
Also, self-tapping screws have structural differences. A regular element, for screwing into metal, requires drilling a hole of a smaller diameter into which the fastener is screwed. To simplify this process, self-tapping screws with a drill tip were developed. They punch a hole themselves, but remember that they cannot cope with thick metal. The drilling head is designed to work with metal up to a maximum thickness of five millimeters.
What other hardware exist?
The above products are only a part of the hardware used in everyday life and industrial purposes. The concept of “hardware” includes all types of metal elements. You can't limit yourself to just fasteners. Since sellers try to make it easier for buyers to find the goods they need, only fasteners often fall into the “hardware” group. Initially, metal instruments were also included in this direction, but now they are more often divided into separate groups. In addition to fasteners, the category of “hardware” includes: wires, cables, steel strips, electrodes and tapes.
All hardware can be classified according to strength class. These indicators are recorded in GOST standards. If we consider fasteners made of alloy and non-alloy steel, there are 11 strength classes. You can request information on a specific product from the manufacturer or seller. When designing structures, it is important to correctly select hardware according to technical characteristics.
When choosing hardware, pay attention to its specific purpose, quality and type of material, dimensions, service life and environmental conditions. To solve serious problems, focus on trusted global manufacturers who guarantee high quality hardware.
Bolts and nuts
Bolts and nuts are used for connections in wood structures. Able to withstand even heavy wooden structures, suitable for creating joints of parts on metal structures. The bolt consists of a cylindrical rod with a head. The shank has a thread for a nut. Fastening two pieces of wood with a bolt provides a strong connection.
A washer is installed between the wood and the nut. Due to this, it is possible to prevent deformation of the wood when the nut is clamped. When choosing a fastener, it is important to correctly select the rod diameter, length, finish, purpose, and determine the maximum permissible loads.
Dowel butterfly
This type of butterfly fastener for drywall has a polypropylene structure. Metal fasteners of this type are also very often used. Used for fastening furniture parts and various wall decoration elements.
Before fastening the part, a hole is made (drilled) in the plasterboard wall to match the diameter of the dowel. The parts, slightly reminiscent of wings, very clearly fix the part inside the plaster middle, thereby preventing the screw from scrolling.
Species diversity
If you try to consider what hardware products are, the photos of railway bolts will be different. This is not confusion or an error, there are simply plenty of subtypes of this fastener in the railway sector. WE WILL go through each one.
Terminal
It is used to connect the lining to the base. It is made of reinforced concrete, so the retainer requires high strength and considerable thickness. It is connected, accordingly, by a terminal. The most commonly used size is 175 mm. In this case, the mass will reach 0.6 kilograms. Used in KB 50 and 65 mounts.
To study the product, pay attention to the markings located on the head. The application is indicated by the letter “K” or “M”. But next to it is a set of numbers - this is the year of production. Although this is not a direct indicator of service life. After all, it depends on the environment in which the bolt will be used. If we are talking about marshy, cold areas, as well as with high train traffic, the shelf life is significantly reduced.
Mortgage
Interlocks the rail with the pad. Also used as an assembly, a nut is required in the kit. The most common type is M22175mm.
Palmate
One of the few fastening options, the quality of which is assessed according to technical specifications, and not according to GOST. At the same time, all its components from the collection, nut, washer, are already assessed according to the state standard.
Its shape is unique and visually easily distinguishes from analogues. Instead of a hat, a forged paw is used. That is, a small metal layer on one side.
Butt
Almost the most massive sample in our review. They are intended for coupling two-headed pads. And its declared standard size is M27x160. Accordingly, the weight also becomes quite decent - 0.818 kilograms. It is worth remembering that the need for such a resource arises only if R-65 pads are used.
How to choose a mount for different shelves
They are chosen based partly on the preferences of the owners and designers, the main criterion being the functionality of the product. When the choice of the main part is made, select the desired fastener.
Tree
It is convenient to hang wooden products on hidden elements, or put them in wide loops.
Wood products
The installation of wood on forged mensolo holders looks good in the overall classic design style. They can be painted in black, copper or bronze tones for a nice look.
Glass
It is not recommended to drill or cut through glass shelves, so holders with clamps will be the solution. Glass is inserted inside them, pulled together tightly, and the shelf is securely fixed.
A good option with this operating principle is the “pelican”. These holders are represented by two large separate parts located at a distance from each other. A shelf is placed between both parts and tightened to fix it with a common screw.
Glass shelf
Sometimes aluminum horizontal profile slats are used. If the shelves are sandblasted, you can install additional lighting.
Corner products
The shelves located in the corner of the room are attached according to the general principle with the difference that the holders are placed at an angle relative to each other.
This is the main reason why long horizontal brackets are not used - they will intersect and overlap.
Corner model
It is necessary to choose aluminum slats, “pelicans”, or similar fastenings. It is worth remembering that corner parts assume a low load.
Metal
Metal ones are mounted on systems that are frames. They are formed from horizontal and vertical slats to which brackets are attached.
Metal model
A simple model involves lifting a load of up to 60 kg, the reinforcement from below holds up to 120 kg, and the placement of the amplifier at the bottom and top adds stability up to 180 kg.
Plastic
Light plastic products are often hung in the bathroom, less often in other rooms.
When tiling walls, you need to follow the rule - the fewer holes drilled, the better.
Plastic model
Plastic cannot support heavy weights, so any type of fastener can be used.
Main types of fastening hardware
Metric fasteners
Made according to approved technical specifications, has a certain thread pitch. Divided into types of parts:
Steel bolt
Consists of a body of a certain length and diameter. The thread is applied mechanically on a lathe. It can cover the surface completely or only a part, defining the working section.
The heads are made in the form of tetrahedrons, hexagons, and octahedrons according to the classical model.
There are heads for special keys with hidden applications; asterisk, straight spline, cross-shaped slot.
Steel nut
Used with bolts to fasten parts. It is a product with a metric hole and internal thread. The outer part is made in the form of polyhedra.
According to the design, it can be in the form of a cap, an elongated coupling, it is possible to have fastening antennae, or in the form of a crown to be able to fix it with a pin from unscrewing.
Steel washer
A fastener that looks like a flat circle with a metric hole. Used in bolt and nut assembly.
They serve to increase the nominal support area of the head of a bolt or nut. Prevents deformation of the surfaces of parts and spontaneous loosening of fasteners.
According to their configuration, they are flat, reinforced, wedge-shaped, spring with a cut, with fixing plates, with toothed notches.
Eye bolt
Fasteners for special purposes. It differs from a regular bolt by the presence of a cast reinforced ring instead of the usual head.
Used as an independent rigging element.
Rivets
These are products for rigid fastening of parts. The main difference is in the material of manufacture.
Aluminum ones are mainly used for cold riveting of structural parts with low and medium responsibility.
Steel and cast iron hardware are mainly used for hot riveting in the manufacture and assembly of high-strength objects.
Nails
A nail, in the usual sense, is a piece of metal rod, sharpened on one side and flattened on the other. The main area of application is the connection of wooden elements, but nails cannot be clearly categorized as “mass-use fasteners”, since there are hardware designed for fastening polymers and composites. They differ both in design and in the materials used in their manufacture.
In fact, a nail is a very broad definition that includes several types of fasteners for various purposes:
- Building. A familiar nail in the classical sense. A metal rod with sharpening and a head without structural features.
- Screw. Has a screw thread along the entire length or part thereof. It can also be hammered and used to fasten wooden blocks subject to increased loads.
- Ruffy. It has small skirts along the entire length or part of it, reminiscent of thread turns, but not connected to each other. Used to connect elements exposed to moisture and deformation. Before driving, a hole of a smaller diameter is often drilled.
- Slate. Designed for fastening slate sheets. Design features include a larger diameter pressure cap and sometimes the presence of a rubber washer.
- Roofing. Designed for fastening roofing materials, and has a disproportionately large head, which ensures reliable fastening of soft coverings.
- Finish and with an oval head. A nail that is completely immersed when driven into the element being fastened. It is used for fixing decorative items, platbands and other things.
In addition, there are furniture fastening, shoe and wallpaper nails, but they have nothing to do with construction or production. Separately, it is necessary to say about nailer nails. They are used in nail guns. Structurally, they are practically the same, but are supplied in blocks connected to each other.
Let's look at the most common fastening hardware
Bolt - is a fastening device for a detachable connection, which is essentially a rod with a thread at one end and a special head at the other (usually 4 or 6-sided).
For the production of bolts, low-alloy, carbon steel, or special steels are used; brass products of other materials are also found.
The thread on the bolt is intended for screwing on the nut.
Bolts are produced with both full and partial threads (relative to the length of the bolt shaft).
Nomenclature of hardware
Fasteners are divided into types:
1. Construction view, consisting of four groups:
• Self-tapping screws
• Metric fasteners
• Anchors
• Dowels
This type includes every fastening element that is used in construction, repair, and so on.
2. Railway type of industrial significance, intended for fastening railway tracks.
3. Plumbing type of fasteners for installation work with plumbing products (toilet, washbasin) The protective function against high humidity and rust formation is performed by nickel and galvanized coating.
4. Furniture view for the connection connector of furniture structures and their connection.
5. Cargo view. Products of this type are used in securing cargo and in installing structures.
6. Anchor type (anchor bolt with a nut, ring, hook) used in finishing works.
7. Electrical installation view. Used in fastening wires and cables.
8. Perforated. Perforated metal plates used for fastening wooden and other structures in construction and everyday life.
Special purpose. Dowels, clamps, rivet nuts and other fasteners used for connecting wires, insulation, cladding and other tasks.
They also include automotive, engineering and other hardware used in specific areas of industry.
General purpose hardware includes metal products used in everyday life: scissors, saws, knives, agricultural products and much more.
Industrial hardware includes a huge number of products, which include fasteners that are used in various areas of industrial activity, railway rivets, steel tape, wire, mesh, ropes, etc.
Due to their specific application, the most common and popular products related to hardware are fasteners, which is why in everyday life it has become common to understand the concept of “hardware” exclusively as fasteners.
Let's look at fastening hardware in more detail.
Fastening construction hardware are divided into two subgroups:
• fasteners with a certain thread pitch (screws, studs, nuts, bolts, etc.).
• fasteners of various configurations and shapes (screws, nails, anchors, staples, dowels, etc.).
Advantages of stainless steel fasteners
To fasten structures and equipment, professionals recommend using stainless steel fasteners. Nuts, studs, bolts and screws made of stainless steel are characterized by high consumer properties.
Stainless steel fasteners have a high degree of resistance to corrosion. A huge advantage is also the resistance to metal oxidation both under normal conditions and in environments of high acidity and high temperatures. Stainless steel products can withstand high physical pressure, which contributes to their long-term use. In addition, stainless steel fasteners have a high level of resistance to fire and temperature changes. Even a fire will not damage stainless metal. Thanks to their shiny appearance without rust or plaque, even after long-term use, elements of such fasteners do not require replacement or repair, therefore they are widely used both in public and private places.
Thanks to its properties, stainless steel fasteners have become indispensable in the pharmaceutical and food industries, as well as in the production of medical equipment. Considering all the advantages of stainless fasteners, it becomes clear why today users choose it.
Return to list
Fasteners and hardware: purpose and scope of application
Fasteners allow you to create detachable and rigid connections. The former can be dismantled and reused; For designs made on their basis, configuration changes are available. The latter are permanent, not implying a change in the position of the fastened elements. Construction cannot be done without fasteners and hardware; railway sector; mechanical engineering; production of cars, electrical products, furniture and other products; installation of electrical wiring, plumbing and heating systems; when carrying out cargo and other work.
Plasterboard fasteners
Bizarre curves of the ceiling, niches with multi-colored lighting and perfectly smooth wall surfaces - plasterboard will help bring any idea to life and turn every room into a work of design art. It has only one significant drawback - making reliable fasteners on a hollow surface is quite problematic. But it is possible with the help of special plasterboard fasteners. The choice of its variety depends mainly on the purpose of the structure.
If you need to hang any light object on a plasterboard partition, for example, a decorative shelf that does not carry a functional load, or a frame with a photograph, you can easily get by with fastening it with self-tapping screws.
To create a more durable fastener, you will need dowels. Especially for mounting in plasterboard, there are several varieties.
The most economical option is a dowel-drive
. Such fasteners can withstand structures subject to light loads. For example, baseboards, window and door frames. It is simple and quick to install, and installation is often accomplished simply by using a hammer.
For objects that are constantly subject to pull-out stress, for example, chandeliers, an umbrella dowel
. It opens up behind the plasterboard sheet in an empty space, distributing the load over a large area.
Universal elements of plasterboard fasteners are the Molly metal dowel
and its plastic counterpart - Molly dowel or butterfly dowel.
The Molly dowel is widely used in everyday life when securing elements of furniture and decor on plasterboard walls and installing lightweight suspended structures. The principle of its operation is simple: when screwing a self-tapping screw into a dowel, the wings of the part open, forming a maximum expansion. In addition, a special cuff is provided to prevent the dowel from turning into the drywall.
Anchors
In their design features they resemble a dowel-nail. The anchor consists of a dowel and a bolt. When the bolt is screwed in, the walls of the dowel expand. Anchors are used to secure large and heavy objects. There is a whole list of types of anchors.
Compression anchors are installed on ready-made non-demountable structures. When installing the frame, a tight fit is ensured between the three parts of the frame - the head, the stop and the hinges. Masonry anchors are used on frames attached to a brick block wall. Anchors with steel studs are attached to steel bases. Wood dowel anchors have one thing going for them: the anchor has clips that are used to wrap and secure it to the wood dowel during installation.
Window fasteners
Plastic windows, when installed correctly, retain heat in the room and protect your home from moisture and cold air. And although the final result is influenced by the qualifications of the craftsman and the quality of accompanying materials, such as glue and foam, only high-quality window fasteners can guarantee the reliability of the connections.
There are 2 main methods for installing plastic windows: fastening to anchors and mounting plates. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and can be used individually or in combination. It doesn’t matter which method is preferable for you, the main thing is to take the choice of window fastening elements seriously.
- they must be resistant to aggressive environmental influences. After all, you have to clean and wash your windows using chemicals, not to mention regular exposure to precipitation. Therefore, the most popular window screws and anchors are galvanized, yellow-passivated, and sometimes oxidized.
- dowels and anchors must be large enough.
Frame anchors
designed for mounting plastic, wooden and metal frames to a brick or concrete base. They withstand heavy breaking and tearing loads, and therefore the anchor fastening is highly reliable, which is so important, for example, when installing heavy balcony blocks.
Mounting with plates
does not violate the integrity of the window profile chambers, which will prevent the double-glazed window from freezing in the harsh Russian winter. But such a fastening may not withstand shock loads when the window is regularly opened and closed, and is used mainly when installing fixed windows.
Window screws
, used when mounting on plates, usually have a sparse thread and a drill-shaped tip. It will greatly simplify your work, as it does not require pre-drilling holes. If there are already holes, window screws with a sharp tip are more suitable. Are you dealing with loose or soft materials? Choose self-tapping screws with large threads, and when attaching the plate to the wall, make sure you have dowels.
And yet, the most widespread option is the combined installation of plastic windows: the upper part of the frame is attached to plates, the lower part is fixed with anchors. Thus, you will ensure maximum reliability of fastening, and at the same time, reduce the share of disadvantages inherent in installation exclusively on anchors.
Cotter pins
These are hardware that have a characteristic eye at one end. The main purpose of such hardware is to prevent self-loosening of bolts and nuts. Initially, the cotter pins are bent to the desired shape to make it convenient to use with other types of fasteners. This type of fastening is used in the construction industry. Cotter pins are characterized by relative flexibility. Universal application and low cost determine increased demand for this category of goods.
The cotter pins are easy to install; you don't even need special tools. Depending on the technical requirements and fastener features, you can choose the appropriate type of cotter pin. Most often, products are made of stainless, carbon and alloy steel. These materials can withstand heavy loads and provide durable corrosion protection.
Roofing fasteners
The reliability and durability of roofing systems depends not only on the quality of the tiles or corrugated sheets, but also on well-chosen roofing fasteners. Since it is he who takes on the main loads both during installation and throughout the entire life of the roof. And incorrectly selected roofing fasteners and violation of installation technology can provoke the onset of destruction of the roofing system in the first year of operation.
The most popular, although new on the construction market, element of roofing fasteners is the roofing screw
. In terms of its technical characteristics, it is significantly superior to a slate nail and can be intended for fastening to both wood and metal bases.
In addition to the usual galvanized hardware, there are self-tapping screws with colored heads. They allow you to select fasteners to match the roof material and make them almost invisible. Roofing screws are also distinguished by the shape of the cap. It can be designed to work with a screwdriver - heads with a cross-shaped or flat section. Or it may have edges that allow it to be used with a special key.
In most cases, to install a roofing screw, you must first drill a hole, especially if it comes to a metal base. For wood, self-tapping screws with a reinforced drill, which are used together with a screwdriver, are quite suitable. Such hardware is fastened securely and quickly. Depending on the base material, the frequency of the thread section also changes. So, for working with metal, it is necessary to select hardware with frequent carvings, and for wood – with rarer ones.
Close attention must be paid to proper installation of self-tapping screws. It is important to ensure that the threaded part of the hardware completely penetrates the rafters and is securely fastened there. The roofing material must come into contact exclusively with the rubber gasket and the screw head. Only then can we talk about the durability and reliability of the fastener.