Fiberboard or MDF, which is better for the kitchen?
- home
- Products MDF Boards
- Laminate
- Product certificates
- Equipment
- Production stages
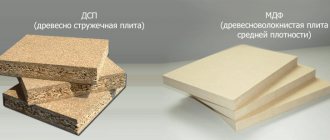
The difference between MDF and chipboard and fiberboard
MDF (MDF-medium-density fiberboard) medium-density fiberboard - This is a board that is made from very fine sawdust.
Fiber boards of uniform thickness are produced from timber and wood waste (offcuts) intended for felling, which are ground into small cubes (chips), subjected to high-pressure steam treatment and subsequently fed to the rotating discs of a defibrator (gritting machine). All wiped material is immediately sent for drying and subsequent gluing. MDF products can be installed in rooms with relative humidity up to 80%, versus 60% for wooden products.
Chipboard (chipboard)
Chipboard - made by hot flat pressing of wood particles (shavings and sawdust) mixed with a binder, mainly synthetic resins (formaldehyde resins). A valuable raw material for chipboard is any low-value wood, both coniferous and deciduous. The performance properties of chipboards mainly depend on their density, shape and size of wood particles, as well as the quantity and quality of the binder.
There are slabs with very low (350-450 kg/m³), low (450-650 kg/m³), medium (650-750 kg/m³) and high (700-800 kg/m³) densities. There are one-, three- and five-layer slabs.
Chipboard is not recommended for use in rooms with high humidity.
This is the most common material for cabinet furniture, interior design, construction (roofs, partitions, etc.).
Pros : water resistance, strength, ease of processing. Chipboard “holds” nails and screws holding the structure together well. Chipboard lends itself well to mechanical processing (sawing, planing, drilling, milling), and is easy to glue and paint. Another advantage of chipboard is its low price. That is why chipboard is the most widely used material for economy class furniture; Most office furniture is made from chipboard.
In some physical and mechanical properties, chipboards are superior to natural wood. In particular, they swell less from moisture; less flammable; do not warp in case of uneven changes in humidity; have good heat and sound insulation properties; more biostable.
Cons: the presence of those very formaldehyde resins that hold wood particles together. The fact is that chipboard releases a certain amount of formaldehyde into the air - not the most healthy product, it should be noted.
There are two types of chipboard: E1 and E2. E1 is more environmentally friendly; its formaldehyde emission rate is noticeably lower. But E2 is prohibited from being used in the production of children's furniture. The most environmentally friendly are chipboards made in Austria and Germany.
The disadvantages of chipboard include the fact that they are heavier than natural wood and are inferior to it in strength.
Fiberboard (fibreboard)
Fibreboard is made by hot pressing of evenly ground wood pulp, impregnated with synthetic resins, with the inclusion of some additives in the mass. The raw material for fiberboard is crushed wood chips and crushed wood, and to improve the performance of fiberboard, paraffin, rosin (increases moisture resistance), synthetic resins (to strengthen the board), and antiseptics are added to the wood pulp.
Like MDF, fiberboard is made from compressed wood dust - but in the case of fiberboard, the wood particles are steamed, and the board is made by wet pressing. That is why the “wrong side” of the fiberboard texture resembles the surface of cottage cheese with a “mesh”, like wet gauze. And that’s why fiberboard slabs are never thick: technology doesn’t allow it. Usually one side of the fiberboard remains like this, and the other is covered with film (laminated or laminated).
There are the following types of fiberboard:
- super-hard (density 950 kg/m³),
- solid (850 kg/m³), semi-solid (400 kg/m³),
- insulation and finishing (250 kg/m³),
- insulating (up to 250 kg/m³) fiber boards.
Fiberboard is a very resistant material to various changes in humidity. The back walls of most cabinets, the bottoms of drawers, these sheets that are rough to the touch are fiberboard. (The most expensive furniture uses plywood instead of fiberboard, but its performance properties are not much better).
Plus: low price with high durability.
Chipboard: characteristics, pros and cons
The most popular material for the production of cheap office furniture, interior decoration, and interior partitions. In general, the scope of use of chipboard coincides with MDF. What is the difference between MDF and chipboard? Thus, to create chipboards, they do not take whole logs or woodworking waste, but wood chips, shavings, and sawdust from low-value tree species (both coniferous and non-coniferous). These shavings and sawdust are hot-pressed and bonded together using formaldehyde or other synthetic resins. These resins are a carcinogenic substance, therefore, depending on the level of their content in the chipboard, their class (and cost) will be determined:
– E1 class chipboard – lower level of formaldehyde emission, that is, carcinogens are not so actively released into the indoor air;
– Chipboard class E2 – high level of emissions into indoor air, prohibited for the production of children's furniture.
By the way, in European countries the production of chipboards of classes E1 and E2 has recently been prohibited; only chipboards of the “Super E” class are produced. As we can see, the difference between chipboard and MDF is also that carcinogenic resins are not used in the production of MDF, unlike chipboard. A very compelling argument.
Chipboard: advantages
– good technical characteristics – chipboards can be sawed, glued, painted
– high thermal insulation and sound insulation properties
- a biologically resistant material that is not exposed to aggressive environments, and with the introduction of special substances it can be moisture-resistant and fire-resistant (but it must be admitted that chipboards are rarely provided with such qualities; almost all chipboards produced by the industry are “ordinary”).
– very hard material. Unlike MFD, chipboard will not be damaged by the fall of a heavy object - there will be no dents left on it
– quite decent appearance, especially when it comes to laminated chipboard. A comparison of laminated chipboard and MDF in terms of decorativeness would be very appropriate: wood-like coatings, multi-colored coatings. Laminated chipboard is resistant to both mechanical and thermal influences. By the way, laminated and laminated chipboard look almost the same, but the former will last much less.
Cons of chipboard
– the biggest difference between chipboard and MDF is the impact on health. Environmentally unsafe chipboards contain carcinogens that affect your health. Yes, there are boards with very low formaldehyde resin emissions. But the phrase “this table is a little carcinogenic” in relation to your children sounds like blasphemy.
– does not hold fasteners well. Once a self-tapping screw falls out, it will fall out all the time.
– impossibility of fine processing (shaped parts, deep milling).
Tel.
- Fiberboard
- Chipboard
- OSP-3
- Laminated plywood
- Plywood FC
- Plywood FSF
MDF is translated into Russian as medium-density wood-fiber pita. Some people interpret the abbreviation as finely dispersed fraction. This material was the result of improvements in the production technology of classic fiberboard.
The material is made from wood that is intended for felling, as well as from waste from the wood processing industry. They are ground to the smallest pieces, steamed, and also rubbed in a special machine. Afterwards, the raw material is sent for drying and gluing. Since MDF particles are glued together with paraffin and lignin, this material is not harmful to human health, and therefore buy MDF
more willing than chipboard.
The advantages of MDF include:
ease of machining,
good sound and heat insulation performance,
uniformity and smoothness of the surface,
constancy of geometric dimensions,
possibility of applying a variety of coatings and decors to the surface.
Do not forget about such advantages as the absence of exposure to mold and fungi, as well as lower cost compared to natural wood.
The MDF profile is a high-quality substitute for wood and acts as an analogue of plywood and wood board. Today there are more than 3 hundred items of a wide variety of products that are created using MDF. Thin sheets of this material are used to make the bottoms of drawers in tables, as well as for the back walls of cabinet furniture. Buy MDF
6-8 millimeters thick can be used for the manufacture of ceiling and wall panels, as well as as a base for laminated parquet flooring. As for MDF with a thickness of 16 to 30 millimeters, most often it is an excellent basis for creating beautiful facades for furniture, piano cases, table tops, etc. But this is not the limit, there are also thicker slabs that are used in the manufacture of external and internal doors, railings, stair steps, etc.
Due to the presence of certain excellent qualities of MDF, it is simply an ideal product that allows you to realize the wildest fantasies of designers. to buy MDF for themselves.
to furnish the interior. Many experts are confident that this is the material of the future.
As for such a material as fiberboard, almost every person who has moved a closet away from the wall in their life is familiar with it. The bottoms of most drawers and the back walls of some types of furniture consist of this material. In more expensive furniture options, fiberboard plants
replaces plywood, but in terms of its characteristics it is only slightly better than wood-fiber sheets.
Just like MDF described above, fiberboard boards are made from compressed wood dust. But in the latter case, the final material is a board made by wet pressing, since wet raw materials enter the press. Therefore, one side looks like cottage cheese, on the surface of which squares of gauze are visible. This is also the reason that fiberboard factories
They can’t make her fat, because technology doesn’t allow anything else. Usually one side of the material remains rough, while the other is covered with a more aesthetic film.
The advantages of such a material as fiberboard include a fairly low cost, despite the fact that the material has a fairly long durability. But there are also disadvantages. We are talking about a small range of areas of use. Naturally, it is impossible to produce a complete set of furniture from fiberboard. But at its post there is practically nothing to replace this material, so many fiberboard factories
They are producing everything just as intensively as before.
Application of materials
Based on the performance properties of each material, the following conclusions can be drawn:
| Material | Optimal area of application |
| Chipboard | Furniture, flooring, partitions, roof and wall cladding. |
| Fiberboard | Interfloor ceilings, floor leveling, roof insulation, partitions in utility rooms. |
| MDF | Furniture, door blocks, carved facades of houses. |
| Array | Furniture. |
We do not take into account laminated chipboard, since it is simply a more expensive variation of chipboard that is heat-resistant.
The table indicates that chipboard, MDF and solid wood can be equally used for furniture production. Clarification is required here.
- Chipboard is good for the production of furniture that must withstand heavy loads in low humidity conditions.
There is no need to worry about the harmfulness of formaldehyde contained in chipboard. Recently, the production technology of this material has stopped using such harmful substances.
- MDF is suitable for installation in the bathroom or kitchen. However, MDF products cannot be placed directly above the stove, as they begin to deteriorate when in contact with temperatures above 70 degrees. MDF is also used when additional decorative surface treatment is planned (for example, cutting out patterns). In the classic style, this material looks somewhat unnatural, but the “unnatural” colors of MDF are well suited for techno, modern and high-tech.
- Solid wood requires a high-quality protective coating for wood. In some cases, it is enough to buy wood oil to protect it from possible rotting and exposure to moisture. Solid wood furniture is suitable for classic and country style.
2013 – 2022 © Progermetik. High quality acrylic sealants
8 INN 7728778367, OGRN 1117746572020 | InfoSystems LLC Privacy Policy | Payment Information
Source: progermetik.ru
MDF or chipboard in the kitchen, which is better?
Kitchen furniture is exposed to temperature changes, high humidity, mechanical stress, household chemicals and other active reagents. The material must resist these negative influences and ensure a long service life.
The most in demand in the manufacture of facades for kitchen furniture are MDF and laminated chipboard. They have some similarities, but differ in composition, production technology, and performance characteristics. To determine which of these materials is best suited for the kitchen, you need to consider the features of each.
Finely dispersed fraction: the beauty of facades
Kitchen furniture made from MDF is in greater demand than furniture made from chipboard. Laminated MDF for the kitchen is often found. These are the same sheets of finely dispersed fraction, but covered with a laminated film to increase the strength and service life of the material. They are the same density and have the same properties.
If a person has a desire to update or make a new kitchen, then it is better to order a kitchen from MDF. The main advantage of this material is environmental friendliness and practicality. While chipboard facades for kitchens require additional finishing with veneer or plastic, MDF facade parts do not need this. And thanks to the paraffin compound, the sheets of the finely dispersed fraction do not emit toxic substances, therefore they are completely safe.
Advantages of MDF boards:
The disadvantage of MDF is the price. The material is cheaper than wood, but more expensive than particle boards. The high cost is due to the lack of resin in the composition, which releases toxic substances. In other words, the material is safer, which is why it costs more.
Kitchen frames
Kitchen frames
- a fulcrum or a reliable foundation. Is it worth overpaying for cases that are hidden from view, or does it not matter what material they are made of? Kitchen cabinets are made from chipboard, MDF, and natural wood.
Are there frameless kitchens? It is difficult to imagine an inflatable kitchen or a stone countertop hanging in the air; rather, it is a suspended kitchen. The KamenStol company makes these too.
But frameless kitchens are still the exception rather than the rule. A hanging kitchen can surprise and make cleaning easier, but it is unlikely to be convenient for the housewife. The kitchen frame is a place for storing dishes and reliable support for the countertop.
CHOOSE THE BEST: MDF OR LDSP FOR THE KITCHEN
Kitchen furniture, compared to ordinary furniture, is a real military training ground. High humidity, cleaning products, impacts, frequent opening and closing of doors, temperature changes - all these are the usual everyday life of a dining room set. Therefore, if you want your new set to last for a long time, choose the material as carefully as you choose the functionality.
Let's look at the most popular options. We suggest you find out what is better for the kitchen: MDF or chipboard.
Facade materials for the kitchen
For the production of furniture sets, MDF, laminated chipboard, mixed frame facades, solid wood, and aluminum profiles are most often used. And if everything is more or less clear with aluminum and wood, then the first two abbreviations raise a lot of doubts and disputes. On the one hand, the use of MDF and laminated chipboard gives designers great opportunities to create an amazing variety of interiors. On the other hand, there are many stereotypes regarding the environmental friendliness and durability of materials.
What are MDF and chipboard made from?
LDSP is a laminated chipboard. To create it, sawdust is treated with formaldehyde resin and compressed. The resulting board is laminated with paper film, which is pre-impregnated with melamine resin. To increase moisture resistance, paraffin or its emulsion is applied to the material.
MDF is a board made from fine wood fraction. The chip size is much smaller than that of laminated chipboard. To produce the material, dried sawdust is pressed, to which paraffin is first added. Due to the fact that the particles are very small, the resulting product is dense and durable. During operation, it does not emit harmful formaldehydes.
Pro et Contra
Which material is better, MDF or chipboard for the kitchen?
Advantages of laminated chipboards • Favorable cost is one of the main advantages of such boards. • Resistant to temperature changes and moisture. • Wide range of colors. The ability to create elegant facades that imitate the texture and shade of different types of natural wood. • Withstands mechanical loads and cleaning with detergents.
Disadvantages of laminated chipboards • High rigidity of the boards, making milling difficult. It is impossible to create facades with complex patterns from such material. • Contains harmful resins, the least toxic type of chipboard is E1 class boards.
Oriented Strand Boards (OSB)
Oriented strand boards are abbreviated as OSB or OSB (from the English OSB - Orient Strand Board). They are made by pressing flat chips at high temperature. Moreover, the chips are laid in layers so that the directions of the fibers in adjacent layers are perpendicular to each other (at right angles). Thanks to this, the material gains special strength.
There are 4 classes of slabs:
- OSB-1 - for dry sheathing;
- OSB-2 - high-strength boards for use in dry conditions;
- OSB-3 - for cladding in conditions of high humidity;
- OSB-3 - high-strength boards for work in wet conditions.
OSB boards are used for the production of sandwich panels used for the construction of frame houses. They are also suitable for leveling walls, floors and ceilings.
Kitchen facades: MDF, chipboard, plastic or solid wood?
Your repost will change the Internet