Among the universal wood-based composite materials, chipboard stands out. The production of particle boards is carried out on production lines of large wood processing plants and small enterprises.
What is chipboard
Chipboard is a sheet material obtained by pressing from small wood shavings, which are held together with glue. The idea of creating such a composite appeared in 1918. Initially, it was proposed to make a slab from shavings with double-sided plywood lining. In subsequent decades, manufacturing technology was refined and improved. The first commercial chipboard production plant opened in 1941 in Bremen, Germany. Widespread use of wood waste boards began after the end of the war.
Interest in the new material is due to several reasons:
- ease of obtaining large-sized parts;
- stability of shape and size;
- using waste as raw material instead of scarce wood.
Thanks to the mass production of chipboard, the amount of irretrievable wood loss during timber harvesting and processing was reduced from 60 to 10%, and the construction and furniture industry received a convenient, technologically advanced and cheap material.
Raw material supplies
Most likely, no one will have problems with the supply of waste wood for chips. If 10-15 years ago such waste was sold to the population as firewood, now owners of sawmills and woodworking industries will be only too happy to get rid of it. If you're lucky, you might even get paid extra for it.
Thermoactive resins can be purchased in any quantity at manufacturing plants in Tyumen, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod - in almost every region of the country. Many entrepreneurs involved in the production of chipboards and related businesses prefer to order thermoactive resin from China. With large volumes of the batch it turns out to be somewhat cheaper than at home. By the way, you can find out what kind of business you can do with China in this source – https://business-poisk.com/chto-prodavat-v-internete-chast-2-top-6-tovarov-iz-kitaya-na -kotoryiy-horoshiy-spros.html.
Types of chipboard
There are several types of particle board:
- pressed;
- laminated;
- moisture resistant;
- extrusion
1. Pressed chipboard has sufficient strength and is used as a structural material in construction and for furniture production.
2. Laminated chipboard is a pressed board lined with a layered coating of paper impregnated with melamine-formaldehyde resins. Lamination increases the surface hardness and wear resistance of the board. A pattern is printed on paper that serves as decoration. During the coating process, it can be given a texture that enhances the decorative qualities of the laminate.
3. Moisture-resistant chipboard, intended for use in damp conditions. Its resistance to moisture is achieved by adding hydrophobic additives to the binder.
4. An extruded (extruded) plate does not have the strength of a pressed one, since it is less compacted, and the chips in it are located perpendicular to the plane of the plate. This material is used for sound insulation.
Pressed laminated and non-laminated chipboard are the most common and popular types. These are the ones that will be discussed further.
Pressed slabs, in turn, are divided according to several parameters: By strength - into groups P1 and P2. The first is general purpose slabs, the second is a material for making furniture and other indoor applications. According to structure – into ordinary (O) and fine-structured (M). For lamination, group M slabs are preferred, since the cladding fits better on them. For surface treatment – polished (SH) and unpolished (NS). In terms of surface quality - grades I and II, for each of which GOST defines a list of permissible defects and their quantity. By emission class - into classes E0.5, E1 and E2. They differ in the maximum permissible formaldehyde content in the material and its release into the air. For indoor use only classes E0.5 and E1 are allowed.
Marketing research
Selling products will not be a problem, but a serious approach to organizing a business will allow you to streamline its volumes and avoid possible miscalculations. Therefore, it is worth conducting marketing research on the market for similar materials in order to more accurately represent the situation in the region.
To do this, you can take the following steps:
- Determine the general need of enterprises for this type of product.
- To track offers of chipboard and its analogues already existing on the market.
- Think about building a marketing strategy for your enterprise (what will be the advantage of the product over others - quality, price, features of the advertising campaign, etc.)
- Consider additional opportunities: business combination, creative approach to advertising, system of individual discounts, etc.
Video on the topic:
Types of chipboard
How chipboard is made
Non-commercial wood and almost any wood waste generated during any processing, starting with tree felling, are suitable for making chipboard:
- substandard round timber and branches;
- slabs, remains from edging boards, trimmings;
- wood chips, shavings, sawdust.
Production consists of several stages.
Preparation of raw materials
Lump waste is crushed into chips. From chips and large shavings, shavings of the required sizes are made: thickness from 0.2 to 0.5 mm, length 5-40 mm, width up to 10 mm.
The round timber is cleared of bark, cut into measured pieces, usually 1 m long, and after soaking, it is split along the fibers into small fragments, followed by grinding to the desired condition.
The plate has a three-layer structure. The outer layers are made from small chips, and the core is made from larger ones. Therefore, the mass of chips is divided and the part intended for the outer layers is further crushed. After drying, sorting occurs. Using sieving, unsuitable fractions are separated and redistributed, and too large chips are returned for grinding.
Molding and pressing
The prepared chips are mixed with synthetic resin, which is included in the chipboard as a binder. This operation is carried out in a special machine, where the resin is sprayed into small drops and settles on the surface of wood particles “suspended” in the air flow. This mechanism allows you to cover the entire surface of the chips with glue and prevent excess resin consumption.
The resinous chips enter the dispenser, which places them on a conveyor belt or pallet, forming a layer of a given thickness. Three layers are laid sequentially, in accordance with the three-layer chipboard structure. The resulting “carpet” is divided along its length into standard size packages and fed into a vibrating press for preliminary compaction. After preliminary pressing, briquettes are obtained that can withstand movement into the main hydraulic press.
Before pressing, the briquettes are heated to 75°C using microwave radiation. In the press they are exposed to a temperature of 150–180°C and a temperature of 20–35 kgf/cm2. Under pressure, the material is compacted, and heat causes the binder to harden.
Full readiness
After pressing is completed, the finished chipboard sheets are cooled by air currents, then stacked and left for several days. During this time, the temperature in the material gradually equalizes and internal stresses are relieved.
Before the material is completely ready, the surfaces are polished and cut into sheets of a given format. They are then labeled and packaged for shipment to the consumer. When producing furniture or facing boards, a lamination stage is added to the technological chain.
Workshop technical equipment
Decide what equipment to buy for the production of chipboards after you decide whether you will use your own raw materials or purchase them from third-party companies. To make chipboard from purchased raw materials, the following devices are used:
- faucets,
- molding machines,
- thermal presses,
- coolers,
- material cutting machines,
- grinding machine,
- drying chambers.
This is the minimum equipment of the workshop. Equipment for the production of chipboards can be either automated or manual - it all depends on the capital available. If you plan to produce chipboard from raw materials obtained within the walls of your own workshop, then additionally purchase:
- cutting machines,
- chippers,
- wood waste shredders,
- planing machines.
Whatever technology you choose, to speed up the process, you will need some additional equipment: conveyors, loaders, conveyors, vibrating screens. As you can see, opening a mini plant for the production of chipboard from purchased raw materials will be less expensive than preparing it yourself. Although this would somewhat reduce the cost of finished products and save time on delivery of the necessary components. Over time, when the enterprise begins to generate stable income from sales, to reduce the cost of the process, all additional machines for preparing raw materials can be purchased and installed in the workshop. The price of equipment for the production of chipboards, fully equipped and automated, with low capacity (up to 100 sheets per shift) is at least 7,000,000 rubles. The cost of lines with more impressive productivity (up to 1000 sheets per shift) can reach up to 15,000,000 rubles. Finding such a large start-up capital will not be easy for beginning businessmen. You can’t do this without a bank loan or the help of private investors. In each case, you will need to draw up a business project to prove to third-party financial organizations the profitability of your future enterprise. It is worth noting that chipboard production as a business can be started with a minimum of costs if you purchase equipment on lease with the right to purchase it later. Also a good alternative to expensive European machines is Chinese equipment. Their quality is no worse, but the price is more acceptable for many entrepreneurs. Modern lines take up quite a lot of space, so look for a room with an area of at least 200 m2 for a workshop. Don’t forget also about warehouses for storing wood components and finished products. Additional space will be required for these needs. The number of personnel directly depends on the capacity of the equipment. For the workshop to fully operate in 12-hour shifts, the staff must consist of at least 10 workers. Industrial line for the production of chipboards:
Standard dimensions of chipboard sheets
The production offers several standard sizes of chipboard sheets:
- 2440x1220 mm;
- 2440x1830 mm;
- 2750x1830 mm;
- 2800x2070 mm.
The last format in this list is not provided for by Russian GOST, but some foreign companies supply laminated sheets of these sizes. The thickness of the material usually corresponds to the standards accepted in furniture production: 10, 16, 18, 22 and 25 mm.
Maximum permissible dimensional deviations according to GOST 10632-2014:
| Thickness, mm | Length, mm | Width, mm |
| +/- 0.3 - for polished | +/- 0,5 | +/- 0,5 |
| -0.3/+1.7 — for unpolished |
Where to sell your products
In addition to offering finished products to large and small manufacturers of cabinet furniture - the main buyers of chipboards - you can also contact enterprises involved in car and mechanical engineering.
Article on the topic: How to paint old furniture with acrylic paint
Your potential buyers may also be construction companies, retail stores of building materials, and wholesale stores. Creating an online resource for the enterprise and placing advertisements in periodicals and specialized publications will provide good assistance in finding buyers.
Main characteristics of chipboard
Strength and density of chipboard
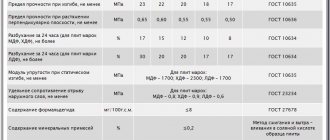
The strength of chipboard is determined by its belonging to one of two groups - P1 or P2. P2 slabs have higher bending strength - 11 MPa versus 10 MPa for the P1 group. They are almost one and a half times more resistant to delamination. The density of sheets of both groups is 550 – 820 kg/m3.
One aspect of strength is the ability to hold fasteners. A screw screwed into the face of the slab can withstand a pull-out load of 3.5 to 5.5 kg per millimeter of length. When installed at the end, the maximum force is less - 3.0-4.5 kg/mm.
| Index | P1 plate | P2 slabs |
| Density, kg/m3 | 550-820 | |
| Impact strength, J/m2 | 4000-8000 | |
| Hardness, MPa | 20-40 | |
| Specific resistance to pulling out screws, N/mm, from the plastic | 55-35 | |
| Specific resistance to pulling out screws, N/mm, from the edge | 45-30 | |
Moisture resistance of chipboard
The resistance of chipboard to moisture is not regulated. This material is intended for dry conditions only. Although there are moisture-resistant versions of it, which are produced with the addition of a water repellent.
Biological resistance
The biological resistance of particle boards is quite high. They are not damaged by insects, and fungus does not take root on them. The slab may completely collapse from moisture, but there will be no rot on it.
Fire safety
When assessing the fire hazard, chipboard should be considered as wood. The composite belongs to the same flammability group G4, although it does not catch fire and spread fire as readily as wood.
Environmental friendliness
Chipboard is quite safe for people, but when using it, you need to pay attention to the emission class, which depends on the level of formaldehyde released into the air. Material of class E2 cannot be used inside residential premises; slabs of class E1 are intended for this. For children's rooms, schools, kindergartens, nurseries, and hospitals, slabs of class E0.5 should be used, which contain a very small amount of formaldehyde and their effect on the composition of indoor air is negligible.
Thermal conductivity
The thermal insulation qualities of chipboard are low, but they should be taken into account when using it as wall, ceiling or floor cladding. The average thermal conductivity of the slabs is 0.15 W/(m∙K). With a thickness of 16 mm, the thermal resistance of the skin per square meter of area will be 0.1 (m2∙K)/W. For comparison: a wall made of ceramic bricks 390 mm thick has a thermal resistance of 2.22 (m2∙K)/W, and a layer of mineral wool 100 mm thick has a thermal resistance of 0.78 (m2∙K)/W. And yet, chipboard sheathing, especially together with the air gap behind it, can become a noticeable addition to insulation.
Vapor permeability
Water vapor permeability is an important characteristic of chipboard if it is used in external building envelopes. With a permeability of 0.13 mg/(m∙h∙Pa), the material cannot serve as a vapor barrier, but when cladding the outside, good vapor permeability will help remove moisture from the wall.
Features of the material
Laminated chipboard contains natural wood - in structure it is chipboards that have undergone high-quality sanding and covered with melamine film. It is this coating that distinguishes the two types of slabs. Laminated chipboard has high moisture resistance and greater strength than conventional boards.
Article on the topic: Do-it-yourself folding chair made from pipes
The laminated surface exhibits greater resistance to mechanical influences, as well as to chemically active substances - acetone, gasoline, alcohol, acids, solvents, coffee. Therefore, furniture made from chipboard can often be found in public places: in reception areas, in offices, in multifunctional centers, in educational institutions, in cafes, in kindergartens, in playrooms and children's rooms, in the kitchen.
The advantage of the material is the variety of its shades and textures
The film not only gives the material excellent performance characteristics, but also allows you to give it a unique appearance - from any shades and textures of natural wood, to images applied according to individual sketches. The ability to choose any shade allows you to produce cabinet furniture for any interior. This is especially true for children's rooms, where bright, rich colors are welcome. Bright furniture is also used for advertising and trade stands, as a body for reception desks with the possibility of being manufactured in the company’s colors with a logo.
Multifunctional cabinet furniture
Note! The laminated layer makes the surface of the chipboard monolithic and does not allow harmful substances that may be contained inside its structure to pass through.
The formation of the laminated layer occurs by pressing paper, which acquires properties comparable to plastic, filled with melamine resin under pressure (up to 28 MPa) and high temperature (up to 210 degrees). Decorative paper impregnated with resin is pressed into the top layer of chipboard.
The surface of such a plate, among other things, is heat-resistant, which allows you to place hot dishes on it - this has made laminated chipboard a popular material for making kitchen countertops.
Manufacturability of chipboard
In terms of convenience and economy of use, chipboard is very much superior to wood. This parameter does not have a numerical expression, but several facts can be cited to illustrate the advantage of chipboard in this regard.
Minimum operations in the manufacture of products
In order to make furniture or other structures from chipboard, you need to perform several basic steps:
- cutting the sheet into parts of the required sizes;
- drilling holes and sockets for fasteners and accessories;
- installation of accessories and assembly.
In many cases, drilling as a separate operation is not available. When using a laminated board, painting with accompanying preparation is not required; only edge trimming is required, which is done on special machines and does not require much effort.
The most difficult operation in furniture making is cutting out parts of complex curved shapes. But the number of such parts is usually small.
Let's compare the above with the actions necessary for a wood product:
- sawing;
- planing;
- fine planing (thicknesser);
- cutting into parts;
- milling, often necessary to connect parts;
- sealing defects;
- grinding;
- painting.
If large parts are required, then the operations of gluing a board from slats or assembling a large part from small ones are added, since the width of wooden boards usually does not exceed 300 mm. Countertops and cabinet doors are made using this method. And this is just the preparation of the parts that need to be combined into a product!
Easy assembly operations
When installing fittings on chipboard parts, drilling for fasteners is often not required. For wood it is required more often, especially for hardwoods. Drilling into chipboard is easier than wood. A slab made from chips is less demanding on the accuracy of installation of fasteners and accessories. All this reduces labor costs in production.
Product stability
Chipboard, unlike wood, does not change size with fluctuations in humidity. Parts made from it will not crack in the summer heat, they will not warp, there will not be an extra gap or a strip of unpainted surface anywhere, as happens with wooden doors. Under normal use, a chipboard product remains unchanged for many years.
Making shelf sidewalls
Let's make the sides of our shelf. On the existing sections of laminated chipboard you need to mark the contours of the shaped parts.
This is easier to do with an improvised compass.
You should start bending not from an arc, but from a flat area of 30–100 mm, otherwise there is a risk of getting an untidy joint when gluing the edge.
Two identical parts can be cut along the same contour by fastening two sheets of chipboard with clamps.
The inner post does not have a top protrusion; it is slightly shorter than the outer one.
Even when using a high-quality file and jigsaw, unsightly chips like these may appear on the edge.
You can get rid of them by sanding the ends with a sanding machine with a sanding belt of K80 or K100 grit.
After sanding the edge looks like this.
Areas of application of chipboard
Chipboard is used wherever large-area parts are required.
Furniture manufacture
Laminated boards are used in furniture production. This immediately removes questions regarding surface cladding. The choice of decors is very large and allows you to satisfy almost any request. Despite some plasticity of the material, the correct arrangement of parts gives the products excellent rigidity.
Most often they are made from chipboard:
Kitchen furniture.
A furniture range is almost always a set of chipboard modules.
Writing and computer desks.
It is convenient to make all kinds of tables, shelves, superstructures, and partitions from flat parts.
Wardrobes, including built-in ones, shelving, filling of dressing rooms.
This furniture is dominated by large-sized parts, and slab material is best suited for this.
In some cases, the weight of the furniture is important. It can be calculated in advance, knowing how much the chipboard sheet weighs, its area, and the total area of the product parts. For example, to make a desk or a small wardrobe you need one standard sheet of 2750x1830 format. With a thickness of 16 mm, it weighs 57 kg. This is approximately how much a table or cabinet will weigh. For a more accurate calculation, you should use the specific gravity of the slab - 11.4 kg per square meter. By tabulating the dimensions of all the parts, it is easy to calculate the weight of the product.
Equipment selection
Technological equipment for production includes the following components:
- Mixer. Designed for mixing raw materials and adhesive to obtain a homogeneous mass.
- Forming machine – for distributing mass among forming containers.
- Presses (pre-press and thermal press) compress the mass.
- Coolers designed to cool the resulting slabs that have undergone high-temperature treatment.
- Trimming machines (vertical and horizontal).
- Sanding machine for smoothing the surface and edges of slabs.
Recruitment
The most responsible and important employee of the workshop is the technologist. A streamlined work process, control and correction of operations depends on his qualifications.
There are several employees under his subordination. So, for example, for equipment with a capacity of up to 300 sheets per shift, 4–5 people will be required. The more powerful the line, the more maintenance personnel will be needed.
Taking into account the size of the premises and the industrial volume of the business, the services of an accountant, driver, security guard and cleaner will be required.